Published 16 January 2024
Behind the Blistering: Delving into the Causes of Pemphigus Vulgaris
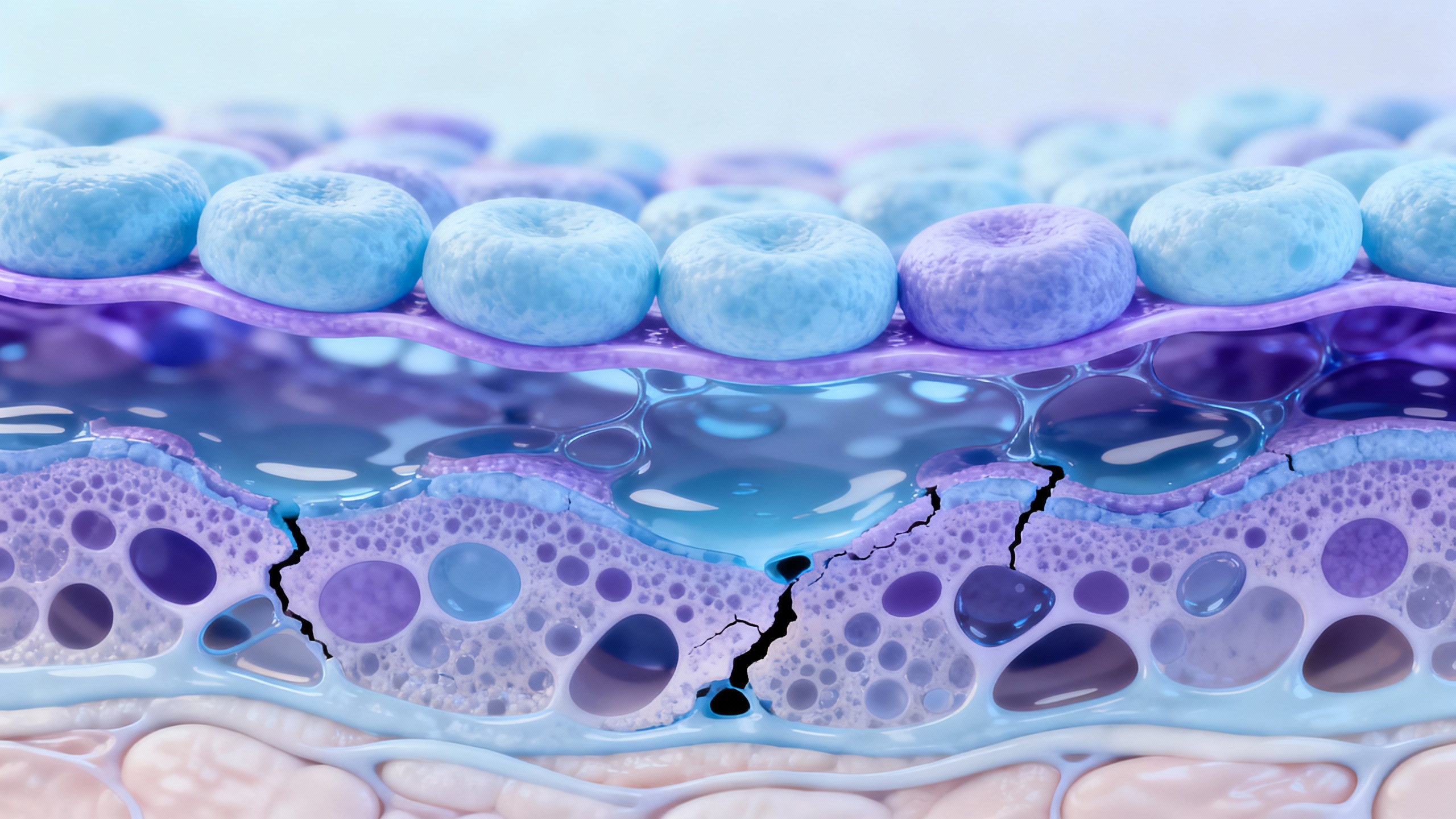
Understanding Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the formation of painful blisters that can rupture easily, leading to open sores and skin breakdown. Understanding the condition and its symptoms is crucial in managing and seeking appropriate treatment.
What is Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the proteins that hold skin cells together. This immune response leads to the formation of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes. Pemphigus vulgaris can affect individuals of any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in middle-aged adults.
The exact cause of pemphigus vulgaris is not fully understood. However, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and autoimmune factors. To learn more about the causes of pemphigus vulgaris, refer to the section on The Causes of Pemphigus Vulgaris.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is characterized by the presence of painful blisters that primarily affect the skin and mucous membranes. These blisters are fragile and can easily rupture, leading to the formation of open sores and erosions. The most common areas affected by pemphigus vulgaris include the mouth, throat, scalp, face, chest, and groin.
Some common symptoms and characteristics of pemphigus vulgaris include:
- Painful blisters that can appear on the skin and mucous membranes
- Blisters that easily rupture, leaving behind raw, painful sores
- Crusty or scaly patches on the skin
- Difficulty eating or swallowing due to blisters in the mouth and throat
- Painful blisters or erosions in the genital area
- Loss of skin color or pigment changes after blister healing
- Itching or burning sensations in the affected areas
If you suspect you may have pemphigus vulgaris, it is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Diagnosing pemphigus vulgaris often involves a combination of clinical examination, medical history assessment, and laboratory tests. To learn more about the diagnostic process, refer to the section on Diagnosing Pemphigus Vulgaris.
Understanding the symptoms and characteristics of pemphigus vulgaris is crucial in seeking appropriate medical care and developing effective coping strategies to manage the condition. For tips on coping with pemphigus vulgaris and relieving pain and blistering, refer to the section on Coping Strategies for Pain and Blistering.
The Causes of Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a chronic autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is important to understand the underlying causes of this condition to effectively manage and treat it. The causes of pemphigus vulgaris can be attributed to autoimmune factors and genetic predisposition.
Autoimmune Factors
Pemphigus vulgaris is primarily an autoimmune disorder, meaning that it arises from an abnormal immune response. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly targets the proteins that hold skin cells together, known as desmogleins. Specifically, desmoglein 3 and desmoglein 1 are the targeted proteins in pemphigus vulgaris.
The exact reason why the immune system begins to attack these proteins is still not fully understood. However, it is believed that certain triggers, such as environmental factors and medications, can activate the immune response and lead to the development of pemphigus vulgaris.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors also play a role in the development of pemphigus vulgaris. Research suggests that certain genetic variations may increase the susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, including pemphigus vulgaris. These genetic factors can influence the functioning of the immune system and contribute to the development of an autoimmune response against desmogleins.
While genetic predisposition is a risk factor, it does not guarantee the development of pemphigus vulgaris. Environmental triggers are typically required to activate the immune response and trigger the onset of the disease.
Understanding the causes of pemphigus vulgaris is crucial for effective management and treatment. By recognizing the autoimmune nature of the condition and the role of genetic predisposition, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment plans and provide appropriate support to individuals living with pemphigus vulgaris.
To learn more about managing the symptoms and blistering associated with pemphigus vulgaris, explore our articles on coping with pemphigus vulgaris and relief for pemphigus vulgaris.
Triggers for Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmune blistering disease, can be triggered by various factors. Understanding these triggers is essential for managing the condition effectively. Two key triggers for pemphigus vulgaris are environmental factors and medications/treatments.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can play a role in triggering or exacerbating pemphigus vulgaris. These factors may include exposure to certain substances or conditions that can irritate the skin and contribute to blister formation. Some common environmental triggers for pemphigus vulgaris include:
-
Sun Exposure: Excessive sun exposure, particularly to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can trigger flares and worsen symptoms in individuals with pemphigus vulgaris. It is important for individuals with the condition to protect their skin by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
-
Heat and Sweating: High temperatures and excessive sweating can irritate the skin and potentially trigger blister formation in individuals with pemphigus vulgaris. It is advisable to keep the skin cool and dry, especially in areas prone to blistering.
-
Chemicals and Irritants: Certain chemicals, harsh detergents, soaps, and other irritants can aggravate pemphigus vulgaris symptoms. It is important to avoid contact with such substances and opt for gentle, fragrance-free products that are less likely to cause irritation.
By being aware of these environmental triggers, individuals with pemphigus vulgaris can take necessary precautions to minimize the risk of flare-ups and promote skin health. For more information on coping and relief strategies, refer to our article on coping with pemphigus vulgaris.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications and treatments can also act as triggers for pemphigus vulgaris. While these triggers are more commonly associated with drug-induced pemphigus, they can also impact individuals with pemphigus vulgaris. Some medications and treatments that have been linked to pemphigus vulgaris flare-ups include:
| Medications/Treatments |
|---|
| Penicillamine |
| ACE inhibitors (e.g., captopril) |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) |
| Certain antibiotics (e.g., tetracycline) |
| Radiation therapy |
If you have pemphigus vulgaris, it is important to discuss your condition with your healthcare provider before starting any new medications or treatments. They can help guide you in choosing alternatives or adjusting your treatment plan to minimize the risk of triggering or worsening symptoms. For more information on managing symptoms and blistering, refer to our article on relief for pemphigus vulgaris.
Understanding the triggers for pemphigus vulgaris is an important step in effectively managing the condition. By identifying and avoiding environmental triggers and working closely with healthcare professionals to minimize medication-induced triggers, individuals with pemphigus vulgaris can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, leading to improved quality of life.
Diagnosing Pemphigus Vulgaris
To properly diagnose pemphigus vulgaris, healthcare professionals employ a combination of clinical examination, medical history evaluation, laboratory tests, and biopsy analysis. This comprehensive approach helps to confirm the presence of pemphigus vulgaris and differentiate it from other blistering disorders.
Clinical Examination and Medical History
During a clinical examination, the healthcare provider examines the patient’s skin and mucous membranes for characteristic symptoms of pemphigus vulgaris. These symptoms include painful blisters, erosions, and raw areas on the skin and inside the mouth. The medical history of the patient is also important in establishing a diagnosis, as it provides valuable information about the onset, progression, and severity of the symptoms.
The healthcare provider may ask questions related to the patient’s medical history, family history of autoimmune diseases, recent medications or treatments, and any known triggers or factors that may have contributed to the development of pemphigus vulgaris. It is essential for patients to provide accurate and detailed information to aid in the diagnostic process.
Laboratory Tests and Biopsy
Laboratory tests are an essential component of diagnosing pemphigus vulgaris. Blood tests can detect the presence of specific antibodies that are associated with the disease. The two main antibodies tested for are anti-desmoglein 1 (anti-Dsg1) and anti-desmoglein 3 (anti-Dsg3) antibodies. These antibodies are found in the majority of pemphigus vulgaris cases and are crucial in confirming the diagnosis.
A skin biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris. During this procedure, a small sample of skin tissue is taken from a blister or an affected area of the skin. The tissue sample is then examined under a microscope to assess the presence of characteristic changes, such as acantholysis (loss of cell-to-cell adhesion) and intraepithelial blister formation.
The combination of clinical examination, medical history evaluation, laboratory tests, and biopsy analysis allows healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose pemphigus vulgaris. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment options can be recommended to manage the symptoms and minimize the impact of the disease on the patient’s quality of life.
For information on managing pemphigus vulgaris and coping with its symptoms, visit our articles on coping with pemphigus vulgaris and relief for pemphigus vulgaris.
Managing Pemphigus Vulgaris
When it comes to managing the symptoms and blistering associated with pemphigus vulgaris, a comprehensive approach is essential. This includes exploring different treatment options, coping strategies for pain and blistering, and making lifestyle changes to support your overall well-being.
Treatment Options
Pemphigus vulgaris is a chronic autoimmune condition that requires ongoing management. Treatment options for pemphigus vulgaris aim to control the autoimmune response, reduce blister formation, and promote healing. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of your symptoms and may include:
| Treatment Options |
|---|
| Corticosteroids |
| Immunosuppressive drugs |
| Rituximab |
| Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy |
| Topical medications |
| Wound care and dressings |
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs. For more information on treatment options for pemphigus vulgaris, visit our article on pemphigus vulgaris treatment options.
Coping Strategies for Pain and Blistering
Dealing with the pain and discomfort caused by pemphigus vulgaris can be challenging. However, there are coping strategies that can help reduce pain and promote healing. These include:
-
Gentle wound care: Cleanse and dress blisters with recommended wound care products to prevent infection and promote healing. Refer to our article on wound care for pemphigus vulgaris blisters for detailed information.
-
Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage pain associated with pemphigus vulgaris blisters. Consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate pain relief options.
-
Psychological support: Living with pemphigus vulgaris can take an emotional toll. Seek support from friends, family, or professional counselors to help cope with the psychological impact of the condition. Our article on psychological support for pemphigus vulgaris patients offers additional guidance.
-
Stress management: Stress can worsen symptoms and trigger flare-ups. Explore stress management techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, or engaging in hobbies to reduce stress levels. Check out our article on stress management techniques for pemphigus vulgaris for more tips.
-
Sleep strategies: Adequate sleep is crucial for overall well-being and can help manage symptoms. Establish a regular sleep routine and create a comfortable sleep environment. For more information, refer to our article on sleep strategies for pemphigus vulgaris sufferers.
Lifestyle Changes and Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatments and coping strategies, making certain lifestyle changes can contribute to the management of pemphigus vulgaris. These changes may include:
-
Diet modifications: While there is no specific diet for pemphigus vulgaris, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet can support overall health and immune function. Consider incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and staying hydrated to support healing. For more guidance, refer to our article on diet recommendations for pemphigus vulgaris.
-
Exercise and physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise, as tolerated, can help manage stress, promote circulation, and support overall well-being. Consult with your healthcare provider for exercise recommendations suitable for your condition. Our article on exercises for pemphigus vulgaris patients provides additional information.
-
Supportive care: Surrounding yourself with a strong support system, including family, friends, and support groups, can provide emotional and practical assistance. Sharing experiences and seeking advice from others who have gone through similar challenges can be invaluable. Explore our article on support groups for pemphigus vulgaris patients for additional resources.
-
Holistic approaches: Some individuals find relief through complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or relaxation techniques. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating any alternative therapies into your treatment plan. For more information, refer to our article on holistic approaches to managing pemphigus vulgaris.
Managing pemphigus vulgaris requires a multidimensional approach that combines medical treatments, coping strategies, and lifestyle modifications. By working closely with your healthcare team and implementing these strategies, you can find relief, improve your quality of life, and effectively manage the symptoms and blistering associated with pemphigus vulgaris.
